
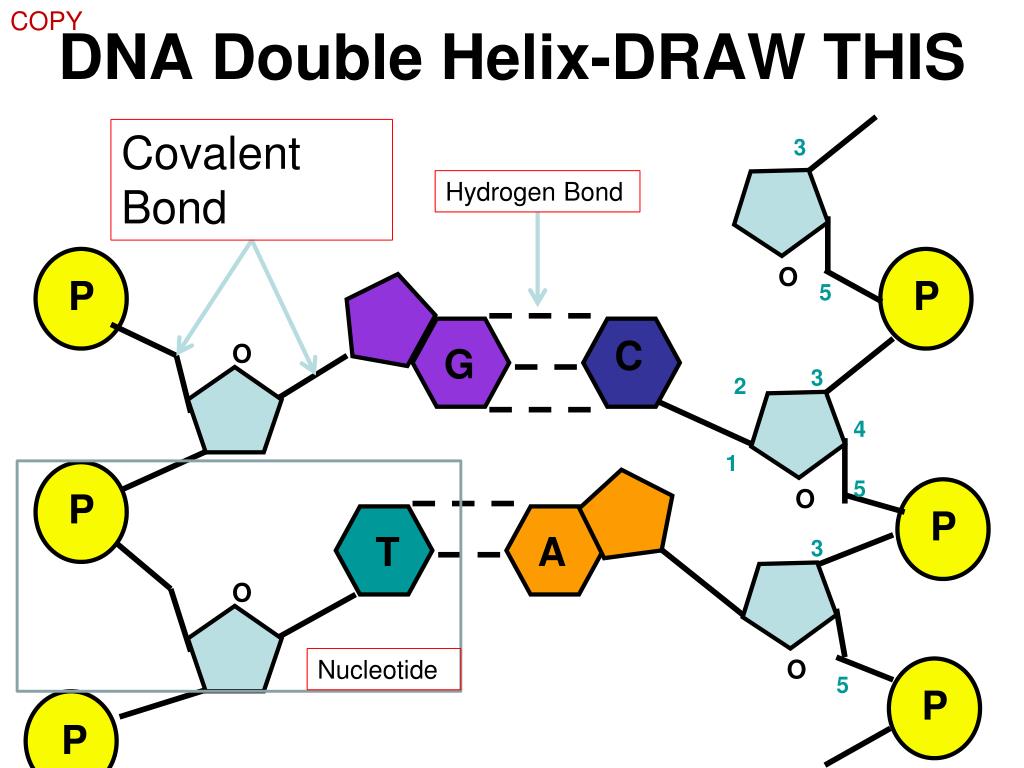
Genetic information is I guess you could say stored in some way. And these rungs are actually where the information, the
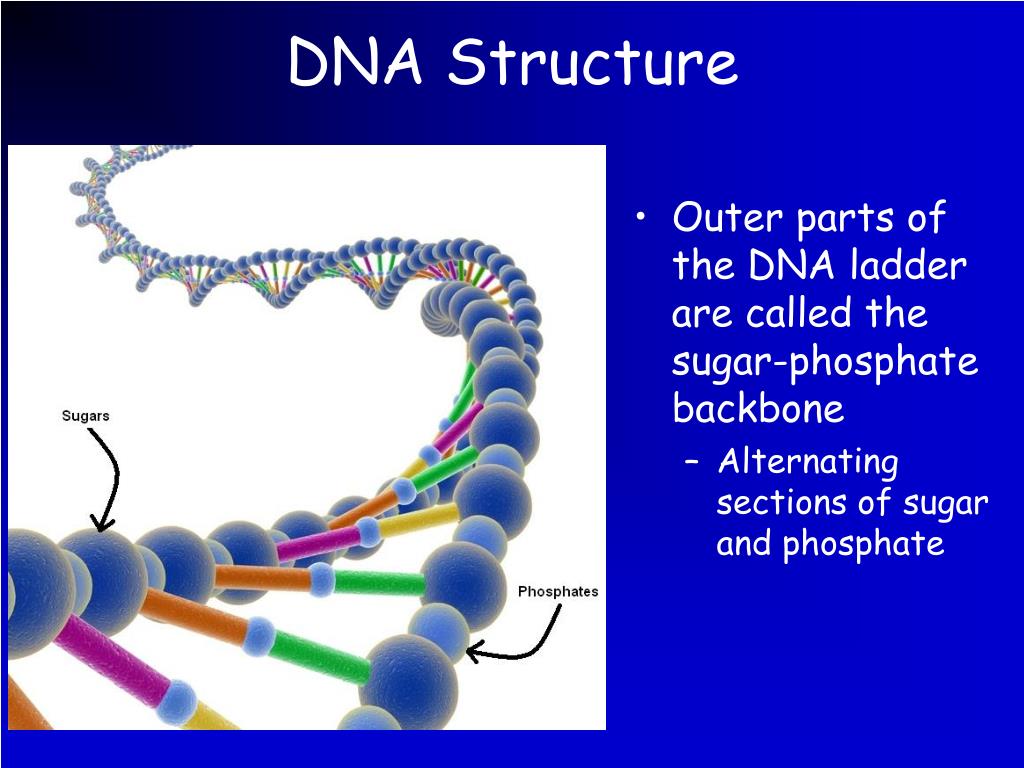
Sides of that twisted ladder you have these rungs. And in between those two sides or connecting those two That is one side right over there and then it is another side. It has these two, I guess you could say sides of the ladder that are twister. So this structure right over here and this is a visualĭepiction of a DNA molecule. We might go in depth on theĮxpression of information in future videos. And then we'll talk a little bit about why this structure lends itself well to something that stores information, that can replicate its information and that could express its information. Looks like our molecule." So first, let's just talkĪbout the structure here and then actually we'll talkĪbout where this name, DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid comes from. But it wasn't until 1953 wherein this double helix structure of DNA was established.
DNA BACKBONE STRUCTURE SERIES
It would have to be a molecule or a series of molecules thatĬould contain information, that could be replicated, that could be expressed in some way. Molecular basis of inheritance." You could imagine what you would need to be a molecular basis of inheritance. And for some time people said, "Maybe this could be a It was this kind of this molecule that was inside of nuclei of cells. Storing the information." Just to be clear, DNA "Hey, that looks like "the molecule that's But it's really the structure of DNA that made people say, The bulk of the data for Watson and Crick's work, Maurice Wilkins and many, On the work of many others especially folks like Rosalind Franklin who essentially provided Not until the structure of DNA was established by Watson and Crick and their work was based Question wasn't figured out until fairly recent times, until the mid 20th century. Even he didn't know exactly what was the molecularīasis for inheritance. How inheritance happened, then you even could start to breed certain types of things. Understand the mechanisms or he was trying to understand But even then, even Mendel who was starting to Way with Gregor Mendel the father of genetics. But it wasn't until theġ800 that that started to be studied in a more scientific For example, someone might have told you, "Hey, you walk kind of like your dad," or, "Your smile is kind of like your mom," or, "Your eyes are like one of your uncles "or your grandparents." And so there's always been this notion of inherited traits. They have noticed that offspring tend to have traits in common with the parent. Human beings have been around I could imagine that


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
